
截止目前,引用Bioss产品发表的文献共34824篇,总影响因子172,562.51分,发表在Nature, Science, Cell以及Immunity等顶级期刊的文献共125篇,合作单位覆盖了清华、北大、复旦、华盛顿大学、麻省理工学院、东京大学以及纽约大学等上百所国际知名研究机构。
我们每月收集引用Bioss产品发表的文献。若您在当月已发表SCI文章,但未被我公司收集,请致电Bioss,我们将赠予现金鼓励,金额标准请参考“发文章 领奖金”活动页面。
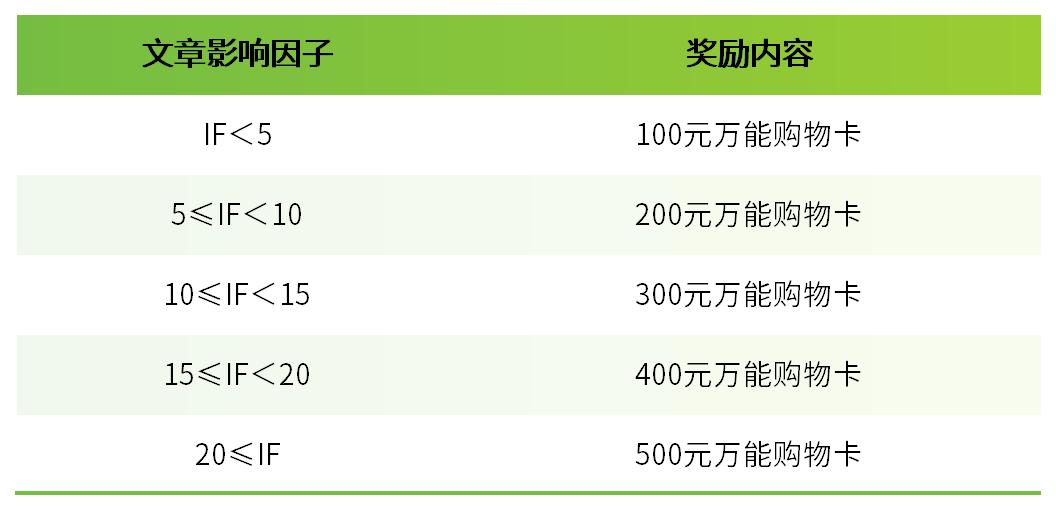
本文主要分享引用Bioss产品发表文章至Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, Nano-Micro Letters, Nature Nanotechnology, Molecular Cancer, Cell Metabolism, Nature Biomedical Engineering, Advanced Functional Materials等期刊的10篇IF>18的文献摘要,让我们一起欣赏吧。
Signal Transduction and
Targeted Therapy [IF=52.7]

文献引用产品:
bs-10197R | nNOS Rabbit pAb | WB
bs-3440R | Phospho-TBK1 (Ser172) Rabbit pAb | WB
作者单位:陆军军医大学大坪医院
摘要:Ischemic/hypoxic injury significantly damages vascular function, detrimentally impacting patient outcomes. Changes in mitochondrial structure and function are closely associated with ischemia/hypoxia-induced vascular dysfunction. The mechanism of this process remains elusive. Using rat models of ischemia and hypoxic vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), we combined transmission electron microscopy, super-resolution microscopy, and metabolic analysis to analyze the structure and function change of mitochondrial cristae. Multi-omics approaches revealed arginase 1 (Arg1) upregulation in ischemic VSMCs, confirmed by in vivo and in vitro knockout models showing Arg1’s protective effects on mitochondrial cristae, mitochondrial and vascular function, and limited the release of mtDNA. Mechanistically, Arg1 interacting with Mic10 led to mitochondrial cristae remodeling, together with hypoxia-induced VDAC1 lactylation resulting in the opening of MPTP and release of mtDNA of VSMCs. The released mtDNA led to PANoptosis of VSMCs via activation of the cGAS-STING pathway. ChIP-qPCR results demonstrated that lactate-mediated Arg1 up-regulation was due to H3K18la upregulation. VSMCs targeted nano-material PLGA-PEI-siRNA@PM-α-SMA (NP-siArg1) significantly improved vascular dysfunction. This study uncovers a new mechanism of vascular dysfunction following ischemic/hypoxic injury: a damaging positive feedback loop mediated by lactate-regulated Arg1 expression between the nucleus and mitochondria, leading to mitochondria cristae disorder and mtDNA release, culminating in VSMCs PANoptosis. Targeting VSMCs Arg1 inhibition offers a potential therapeutic strategy to alleviate ischemia/hypoxia-induced vascular impairments.
Nano-Micro Letters [IF=36.3]

文献引用产品:
bs-0283P-RBITC | Ovalbumin, RBITC conjugated | Other
作者单位:上海交通大学医学院
摘要:Immunization has long played essential roles in preventing diseases. However, the desire for precision delivery of vaccines to boost a robust immune response remains largely unmet. Here, we describe the use of acupoint delivery of nanovaccines (ADN) to elicit dual-niche immunological priming. ADN can simultaneously stimulate mast cell-assisted maturation of dendritic cells at the acupoint and enable direct delivery of nanovaccines into the draining lymph nodes. We demonstrate that ADN not only provokes antigen presentation by lymph node-resident CD8α+ dendritic cells, but also induces the accumulation of nanovaccines in B-cell zones, amplifying antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses and immunoglobulin G antibody expression in draining lymph nodes. ADN also generates systemic immune responses by causing immune memory and preventing T-cell anergy in the spleen. Further supported by evoking effective antitumor responses and high-level antiviral antibodies in mice, ADN provides a simple yet versatile platform for advanced nanovaccination.
Nature Nanotechnology [IF=34.9]

文献引用产品:
V2004 | AFP Mouse mAb | ELISA
作者单位:中国科学院化学研究所
摘要:Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) has been widely used in cancer diagnostics due to its specificity, sensitivity and high throughput. However, conventional ELISA is semiquantitative and has an insufficiently low detection limit for applications requiring ultrahigh sensitivity. In this study, we developed an α-hemolysin-nanopore-based ELISA for detecting cancer biomarkers. After forming the immuno-sandwich complex, peptide probes carrying enzymatic cleavage sites are introduced, where they interact with enzymes conjugated to the detection antibodies within the complex. These probes generate distinct current signatures when translocated through the nanopore after enzymatic cleavage, enabling precise biomarker quantification. This approach offers a low detection limit of up to 0.03 fg ml–1 and the simultaneous detection of six biomarkers, including antigen and antibody biomarkers in blood samples. Overall, the nanopore-based ELISA demonstrates high sensitivity and multiplexing capability, making it suitable for next-generation diagnostic and point-of-care testing applications.
Nature Nanotechnology [IF=34.9]

文献引用产品:
摘要:Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy has revolutionized the treatment of haematological malignancies. Challenges in overcoming physical barriers however greatly limit CAR-T cell efficacy in solid tumours. Here we show that an approach based on collagenase nanogel generally improves the outcome of T cell-based therapies, and specifically of CAR-T cell therapy. The nanogels are created by cross-linking collagenase and subsequently modifying them with a CXCR4 antagonist peptide. These nanogels can bind CAR-T cells via receptor–ligand interaction, resulting in cellular backpack delivery systems. The nanogel backpacks modulate tumoural infiltration and localization of CAR-T cells by surmounting physical barriers and disrupting chemokine-mediated CAR-T cell imprisonment, thereby addressing their navigation deficiency within solid tumours. Our approach offers a promising strategy for pancreatic cancer therapy and holds potential for advancing CAR-T cell therapy towards clinical applications.
Molecular Cancer [IF=33.9]

文献引用产品:
摘要:Colorectal cancer (CRC) liver metastasis is the main cause of cancer-related mortality. How liver influences intercellular communication to support CRC liver metastasis remains unknown. Herein, we link GP73, whose chronic upregulation in hepatocytes triggers non-obese metabolic-dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) in mice, with exosome biogenesis and CRC liver metastasis. Mice with high liver GP73 expression exhibited increased CRC liver metastasis in an exosome-dependent manner. GP73 modulated the cholesterol contents in endosomal compartments to promote exosome production. Quantitative proteomics revealed GP73 reshaped hepatocyte exosomal proteome and produced NAV2-rich exosomes. Clinically, serum GP73 levels positively correlated with exosomal NAV2 levels in CRC patients with liver metastasis. Knockdown of liver NAV2 suppressed enhanced CRC liver metastasis in GP73-induced non-obese mice, and GP73 blockade mitigated the increased CRC liver metastasis in obese mice fed by high-fat diet or high-fructose diet. Our findings suggest GP73 blockade as a potential therapeutic strategy for mitigating CRC liver metastasis.
Cell Metabolism [IF=30.9]

文献引用产品:
bs-1278R | 8-OHdG (DNA/RNA Damage) Rabbit pAb | IF
作者单位:华中科技大学同济医学院
摘要:Atherosclerosis (AS) has been shown to be an independent risk factor for vascular cognitive impairment (VCI), but the mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we found that AS circulating exosomes exacerbated ischemic white matter injury and VCI. Exosomes originating from macrophage-derived foam cells targeted microglia. Mechanistically, foam cell-derived exosomes transmitted redox imbalance, mitochondrial dysfunction, and metabolic defects to microglia via the miR-101-3p-Nrf2-Slc2a1 axis. Anti-miR-101-3p or activation of Nrf2, both genetically and pharmacologically, could antagonize AS exosomes and ameliorate VCI. In conclusion, our findings reveal a distant connection between peripheral macrophages and brain microglia, which provides new insights and potential targets of AS-induced VCI.
Nature Biomedical
Engineering [IF=26.6]

文献引用产品:
bs-0295G-BF647 | Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L,BF647 conjugated | IF
作者单位:中国科学技术大学第一附属医院
摘要:The delivery of nanoparticles (NPs) into solid tumours is challenged by the tumour vascular basement membrane (BM), a critical barrier beneath the endothelium with robust mechanical properties resistant to conventional treatments. Here we propose an approach that uses nitric oxide (NO) to induce the opening of endothelial junctions, creating gaps between endothelial cells and enabling the navigation of NPs through these gaps. Subsequently, NO orchestrates a transient degradation of the BM encasing NP pools in a precise, localized action, allowing the enhanced passage of NPs into the tumour interstitial space through explosive eruptions. We have engineered a NO nanogenerator tailored for near-infrared laser-triggered on-demand NO release at tumour sites. Through breaching the BM barrier, this system results in an increase of clinical nanomedicines within the tumour, boosting the tumour suppression efficacy in both mouse and rabbit models. This approach delicately manages BM degradation, avoiding excessive degradation that might facilitate cancer metastasis. Our NO nanogenerator serves as a precise spatial catalytic degradation strategy for breaching the tumour vascular BM barrier, holding promise for NP delivery into non-tumour diseases.
Advanced Functional
Materials [IF=19]

文献引用产品:
作者单位:郑州大学附属儿童医院
摘要:In vivo optical tumor molecular imaging encounters significant challenges in achieving adequate tumor specificity and sensitivity, largely attributed to off-tumor signal leakage and the relatively low expression levels of target molecules. Therefore, a double self-amplified programmable allosteric DNA nanomachine (named HPs-tFNA) is developed through two elaborately designed hairpin structures (HP1 and HP2) hybridized on tetrahedral framework DNA (tFNA), enabling rapid, specific, and sensitive tumor molecular imaging using the highly specific expression of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) in the tumor cytoplasm as a stimulus-response target. In the presence of APE1, HP2 modifies two apurinic/apyrimidinic sites (AP sites), which can be specifically recognized and cleaved by APE1, releasing a significant number of cyclic sequences (cyclic-seq) and achieving initial APE1-assisted signal amplification. Subsequently, cyclic-seq hybridizes with HP1, inducing a conformational change that converts the stem-loop structure of HP1 to a linear form. This structural change facilitates the spatial separation of the fluorophore and quencher, thereby generating fluorescence signals. Furthermore, APE1 incises two AP sites within the HP1 loop region, resulting in the release of cyclic-seq. The released cyclic-seq can hybridize with additional HP1 to continuously amplify the fluorescence signal in a cyclic manner, thereby achieving the second round of signal amplification assisted by APE1. The experimental results of this study demonstrated that HPs-tFNA can achieve rapid in situ tumor molecular imaging and guide precise surgical excision in vivo, with superior spatial specificity. In particular, HPs-tFNA can effectively monitor drug resistance in neuroblastoma cells and stratify risk levels of neuroblastoma via plasma analysis.
Advanced Functional
Materials [IF=19]

文献引用产品:
作者单位:中南大学
Advanced Functional
Materials [IF=19]

文献引用产品:
bs-5570R | phospho-PI3KCA (Tyr317) Rabbit pAb | WB
作者单位:温州医科大学附属第二医院
